Switching From Wordpress To Hugo

Here are all my posts listed in reverse-chronological order. (If you don’t have your Ad Blocker on, you might see Ads, which ended up being money in my pocket)
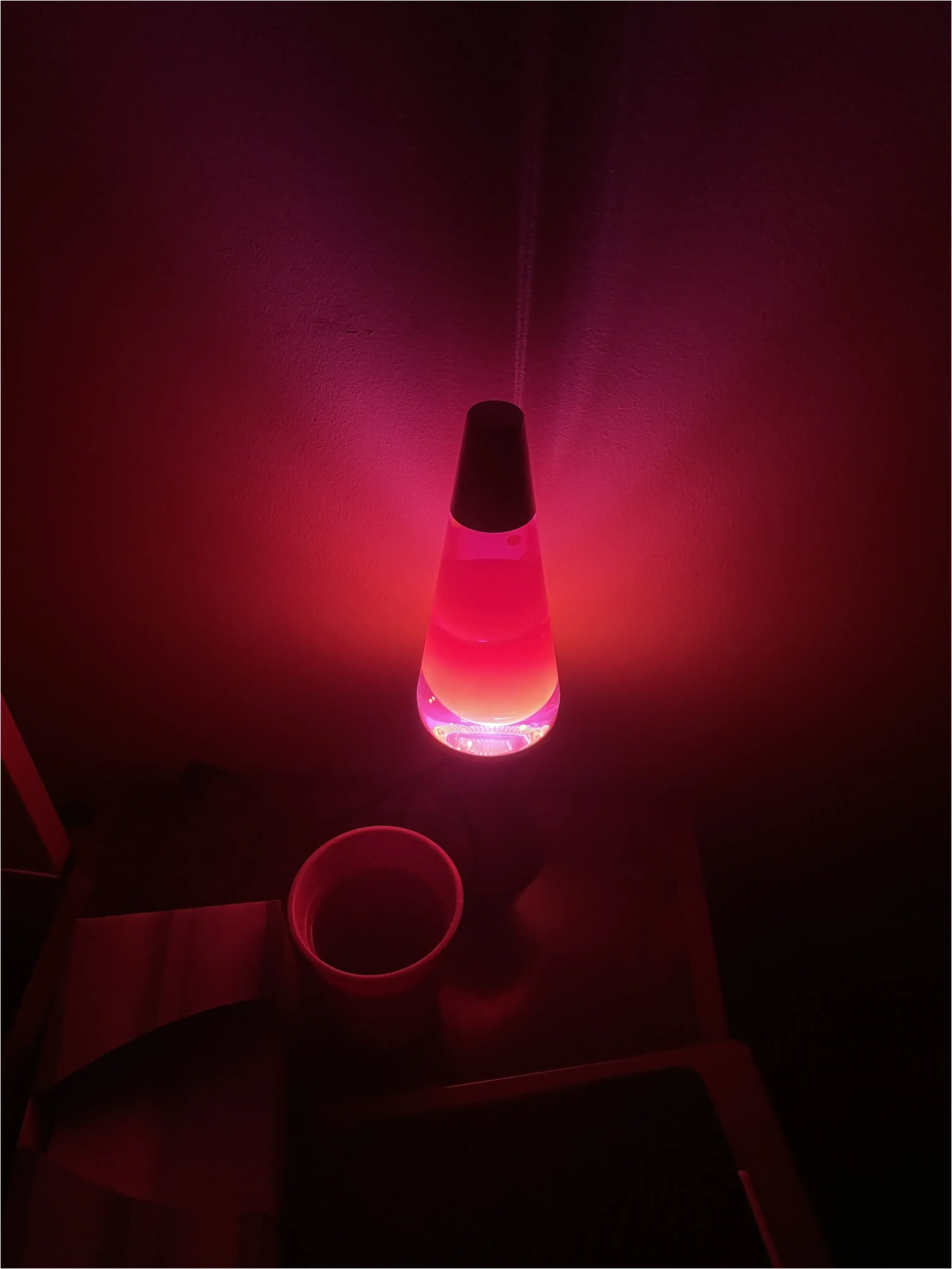


Having real randomness on a deterministic machine is a pretty interesting topic, while one can easily achieve pseudo-randomness by creating a complex algorithm with unpredictable outputs(such as a chaotic system). However, for a microcontroller with the same code whenever it boots up, the above solution will give you the same number every time. So it would be nice to introduce some external chaotic sources, the most commonly used one might be heat noises, which require some kind of temperature sensor. I also heard Lava Lamps are being used as a chaotic source in some real applications - Cloudflare uses 100 such lamps for their random generator - how bizarre!
GAN(Generative Adversarial Network) is a Neural Network model in which there exist two neural networks, one commonly referred to be the Generator and the other as Discriminator. Adversarial Learning is a study of attacking neural networks, but it is being used as a tool to build the GAN model. In each iteration, the Generator will synthesize a product–commonly to be images in modern applications, and the Discriminator will take this product as input and judge if this product is real or fake(produced by neural networks); if it is the second case, the parameters of the Generator will be tuned, the goal is making the product as realistic as possible.
When playing with my RP2040, following the official SDK instructions, I wonder why I have to type cmake then do make, why does it take two steps to build my project?
Well, long story short: Cmake is a cross-platform Makefiles generator, while make “reads the makefile and invokes a compiler, linker, and possibly other programs to make an executable file.(Microsoft)
Instead of thinking of CMake as a “C/C++ program maker,” I tend to say it as a “Cross-platform maker.” As its design principle says: “CMake is designed to be used in conjunction with the native build environment.”(Cmake.org); thus, it is independent of the Operating System it is working on(thus, the compilers), Which means as long as we configure the CMakeLists.txt correctly, CMake should “generate standard build files (e.g., makefiles on Unix and projects/workspaces in Windows MSVC).” on all the supported OS(Cmake.org)

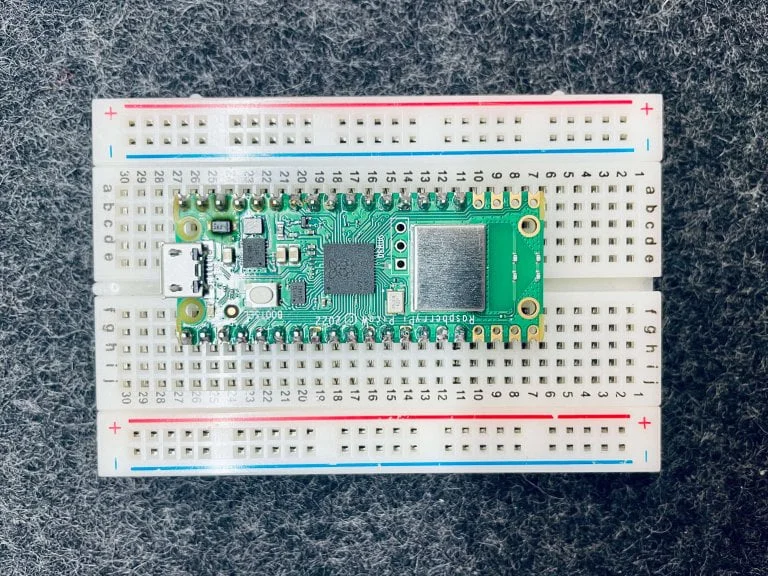
I’ve been pretty into the Raspberry Pi Pico family lately—it looks nice, and it’s new, there is a fast-growing community there, and it would be cool to play together. Pico W is the newer member with the…well, you guess…the Wireless capability. I thought it would be nice to set up some code to allow me to send data from the terminal to the Pico through wifi.
This is an Arduino Core for the Pico, which based on the official Raspberry Pi Pico SDK but with more add-ons. That basically allows you to use Arduino libraries. You can find their Github link here and the latest documentation here. This project is very active.
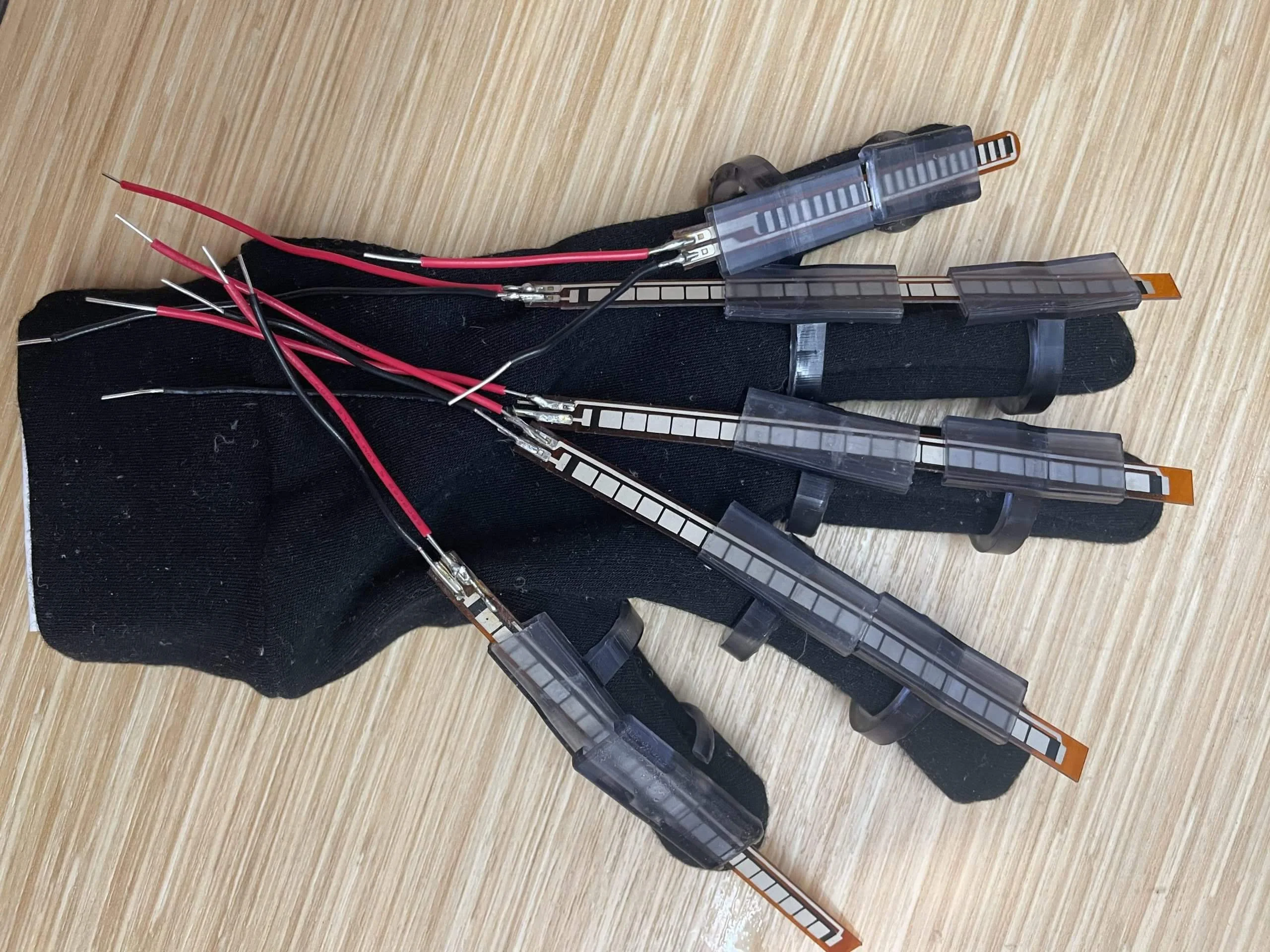

So one day, I was casually browsing the Adafruit Wbsite, and one thing just popped in front of me…

Hi,
This site has been operating for almost 5 years, and I’ve moved to the United States for College. The original site was hosted on a cloud server in Hong Kong, and now the new Hosting Service would be provided by Vultr at Silicon Valley. Meanwhile, I added two domains: DeemoChen.com and YizhouChen.com, both of them would be redirected to the master domain DeemOcean.com.
In the near future, cool functions will be added as the site becomes alive again.
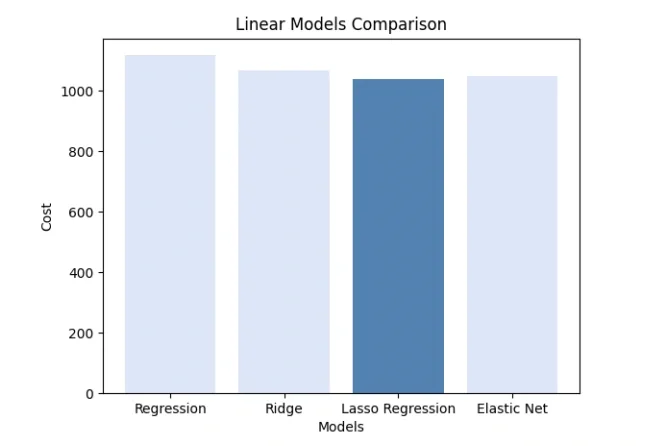
This paper discovers the advantages/disadvantages of different ML models dealing with a particular dataset.
For a general optimization problem, it usually could be rewritten as maximizing or minimizing a certain function with several constrictions. For example, maybe you want the optimized value non-negative. The most basic form of such is called the primal question which looks like this:
$$ \begin{matrix} \underset{x}{min}f(x), x \in \mathbb{R}^n \newline s.t. \newline g_i(x)\leq 0, i=1,2,…,m \newline h_i(x)= 0, i=1,2,…,p \end{matrix} $$
For simple linear regression:
$$ E\left ( Y|X=x \right ) = \alpha +\beta x $$
we have:
$$ \hat{\beta } = \frac{cov\left ( X, Y \right )}{var\left ( X \right )} $$
$$ \hat{\alpha} = \bar{Y} - \hat{\beta}\bar{X} $$
We can all use the NN method to solve the regression problem but that leads to being nearly impossible to locate exactly which layer foreshadows which feature of the data. Thus, maybe the better way is to upscale the dimension of the linear regression method. That, we not only use $ x $ but $x, x^{2}, x^{1/2}… $to approach the true curve.